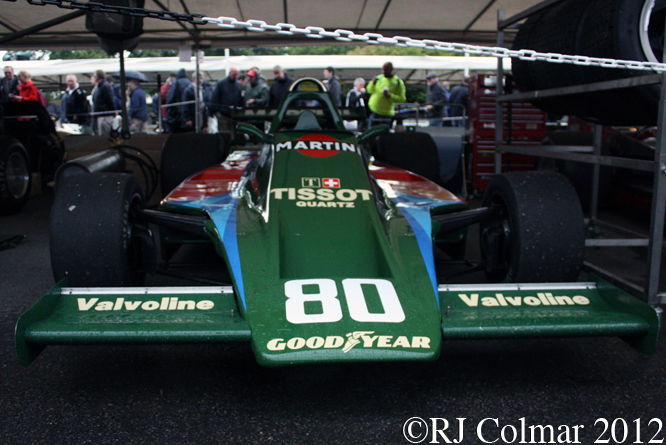
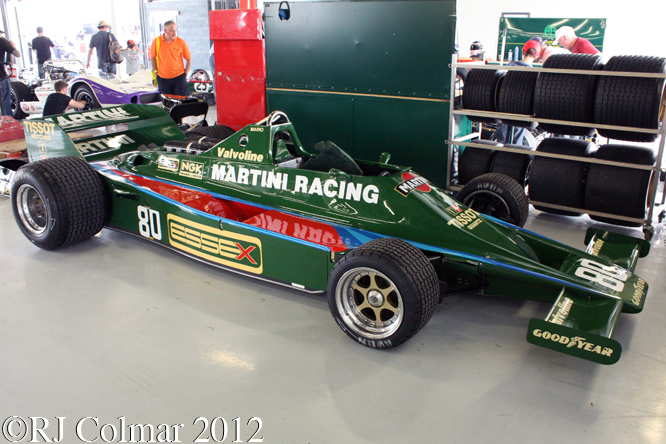
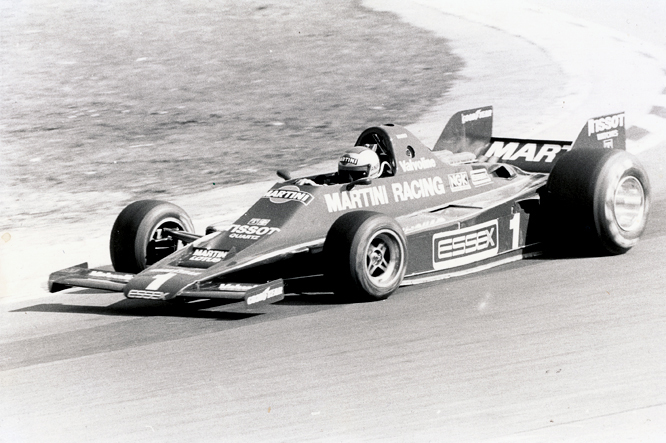
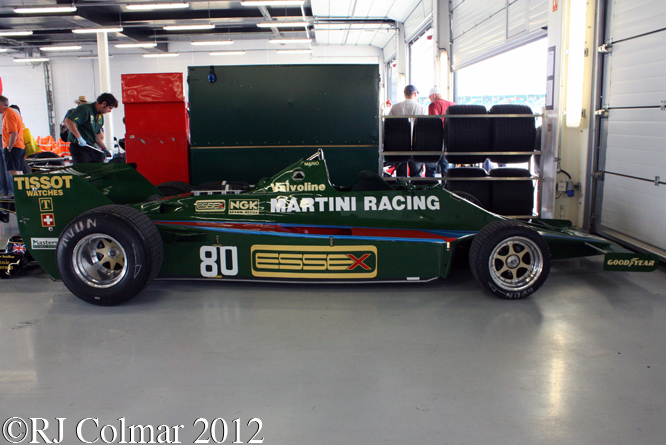
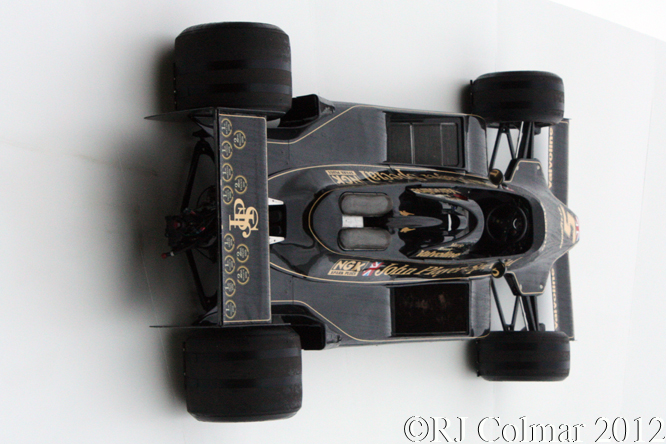
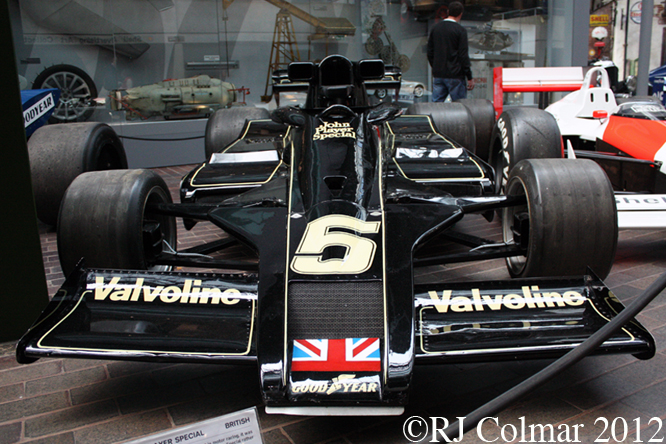
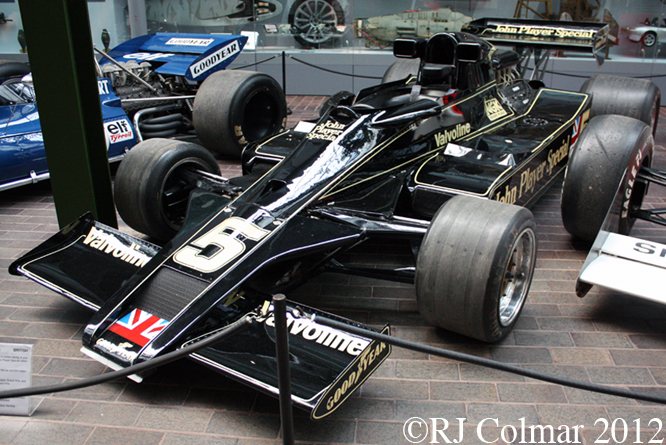
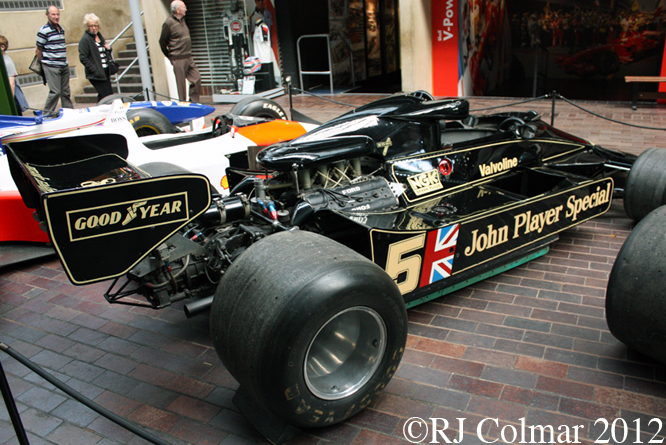
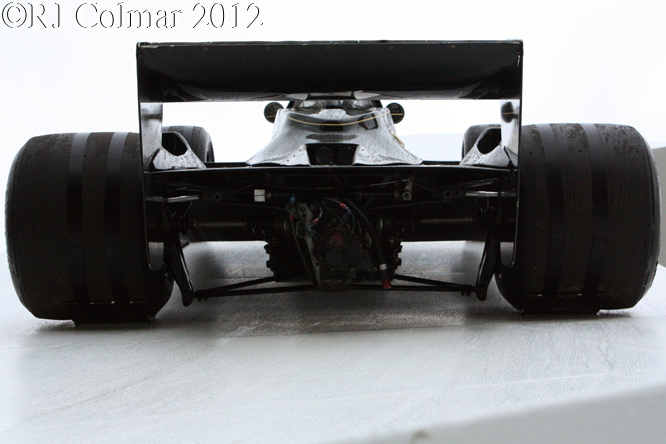
Today’s post features a few of my favourite Formula One ’74 to present day cars that appeared at Goodwood last week.
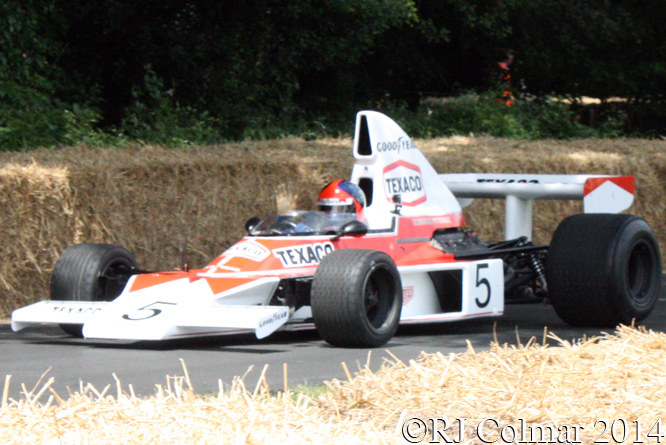

First up Emerson Fittipaldi gives GALPOT a wave coming back down the hill in his 1974 McLaren M23 chassis #5.
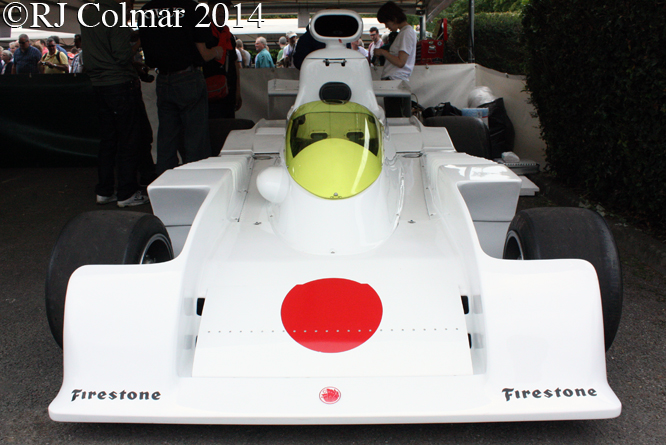

After Honda’s disappearance from the Formula One grid at the end of the 1968 season there was no Japanese presence in Formula One until the 1976 Japanese Grand Prix. However this was not for the want of trying, Kenji Mimura founded the Maki Team in 1974 and their futuristic F101, which bore a passing resemblance to the experimental 1972 Ferrari 312 Snowplough attempted to unsuccessfully to qualify for the 1974 British and German Grand Prix. After Howden Ganley broke his legs at the Nurburgring the team retired to Japan to rework their ideas for 1975.
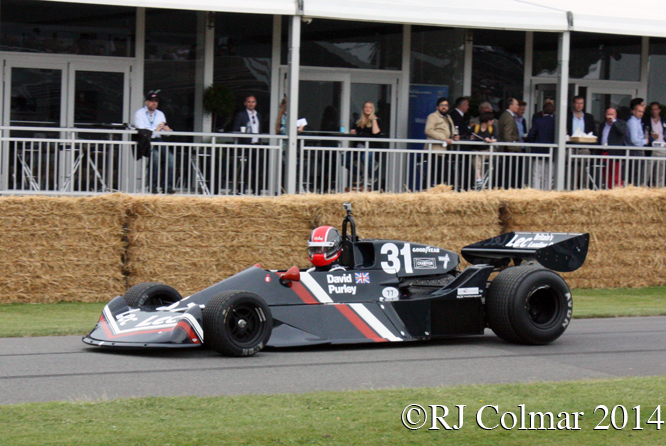

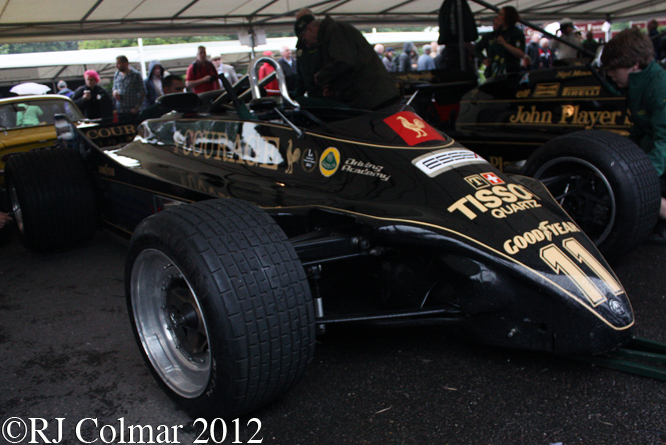
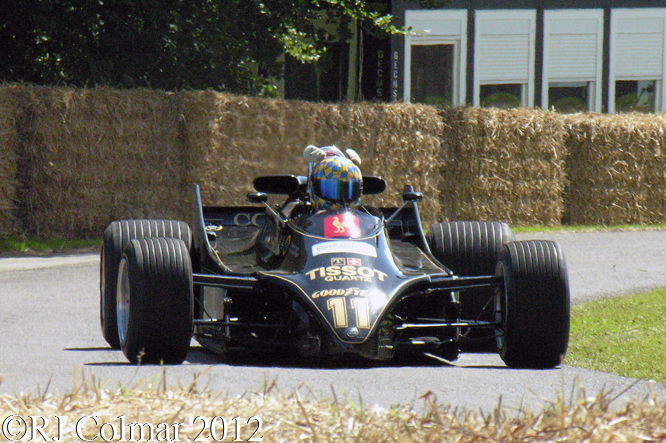
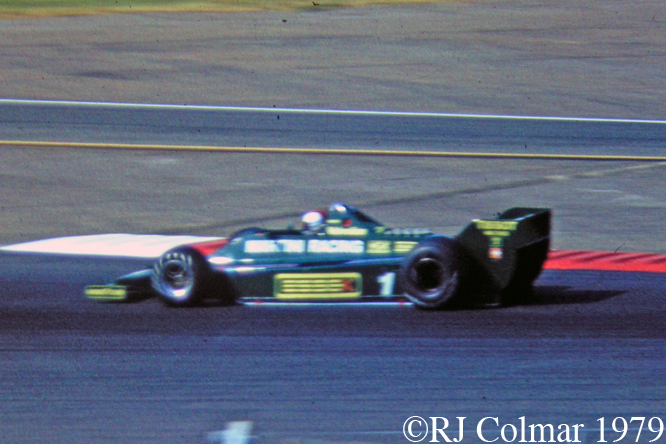
Mike Pilbeam’s portfolio of attractive Formula One cars includes the LEC CRP1 seen above which was driven by David Purley in 1977 to a season high 13th place in Belgium shortly before surviving a 178 g deceleration from 108 mph to 0 in 25 inches / 66 cm against the sleepers during practice for the 1977 British GP. This particular car driven by Gary Wright had not been seen in action for 35 years.
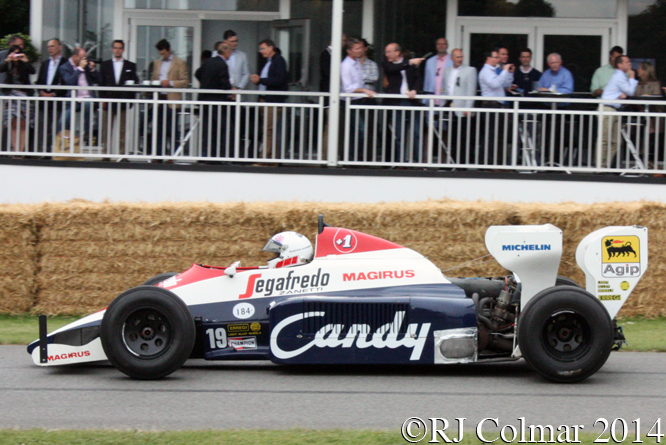

There were numerous vehicles which Ayrton Senna had driven present at Goodwood, and the Toleman TG184 above driven by Alistair Davidson may be one of them, an acquaintance who has spent twelve months researching the TG184 chassis tells me each of the five TG184’s has a slightly different rivet pattern where the roll bar connects to the top of the monocoque and is currently looking for body off photo’s of the TG184’s to confirm which car is which.
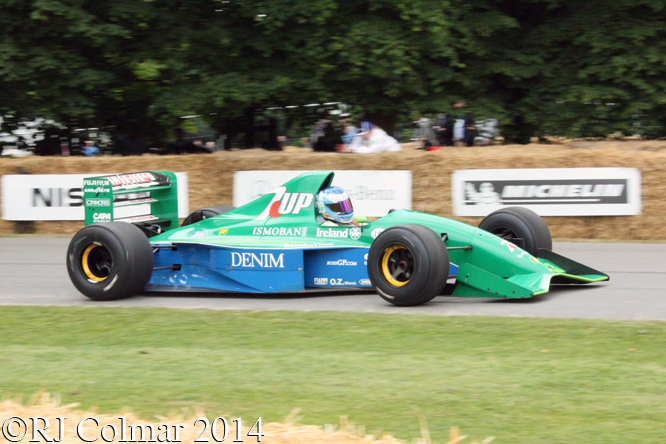

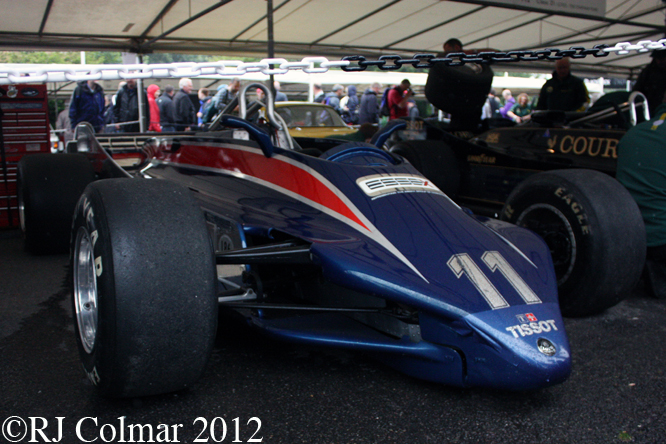
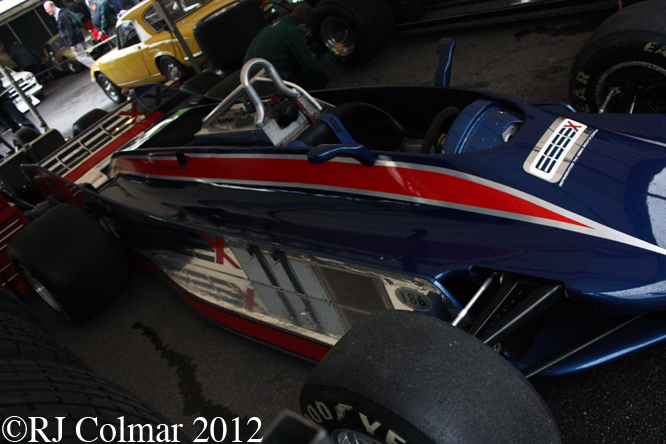
In 1991 Eddie Jordan graduated to Formula One with one of the most attractive Formula One cars ever seen, designed by Gary Anderson, a fist full of Pepsico dollars, works supplied Ford Cosworth engines and Andrea de Cesaris as his lead driver. The team finished a highly creditable 5th in the constructors championship and Andrea 9th in the drivers championship. The team will also be remembered for introducing Micheal Schumacher to the top table of the sport in Belgium. Owner Didier Sirgue is seen at the wheel above.
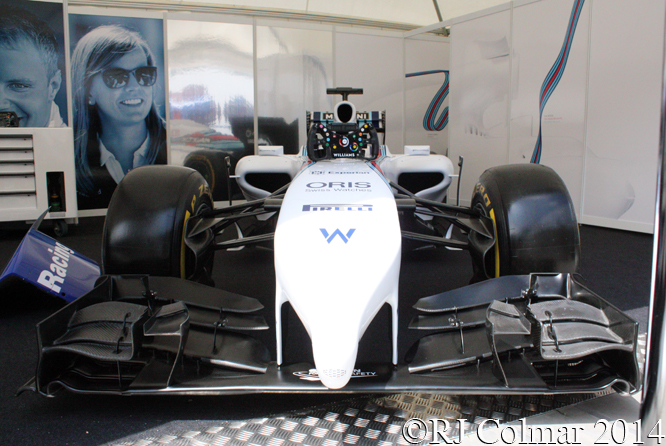

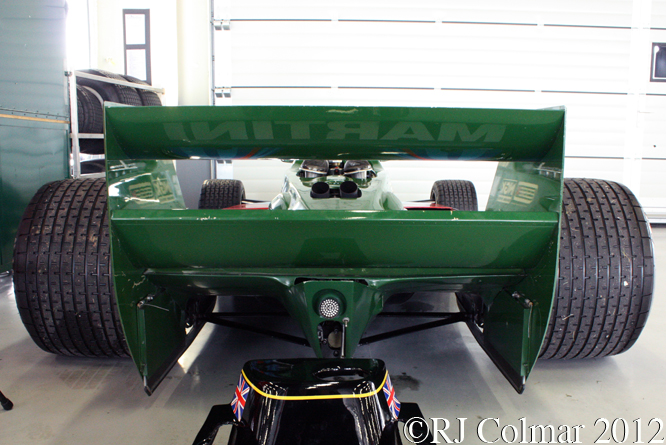
Finally with Mercedes Benz motors and Martini money the Williams team is back on the ascendent this year with Felipe Massa and Valtteri Bottas at the wheel. The FW36 above unfortunately had to remain silent to avoid contravening the no testing agreement currently in operation amongst Formula One teams.
Thanks for joining me on this “Goodwood Favourites” edition of “Gettin’ a li’l psycho on tyres” I hope you will join me again tomorrow when I’ll be celebrating the 120 Anniversary of Motorsport participation with Mercedes Benz at Goodwood. Don’t forget to come back now !