The story of the Lotus 49 in all of it’s guises is inextricably linked to the one component that was a decade ahead of it’s time the Ford DFV motor, which did not win it’s last race until 1983 and was still being used in 1985 running against turbocharged powered cars.
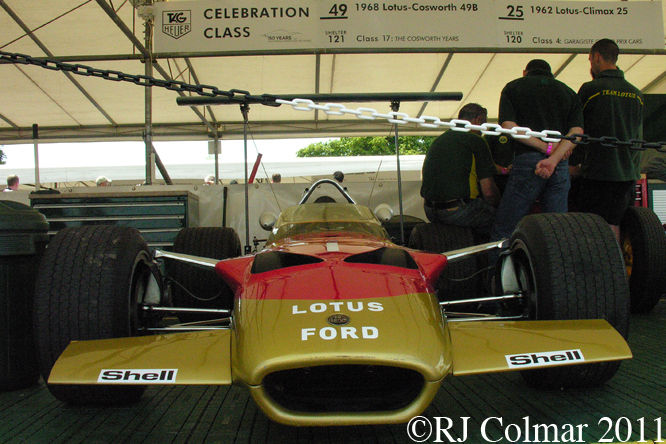

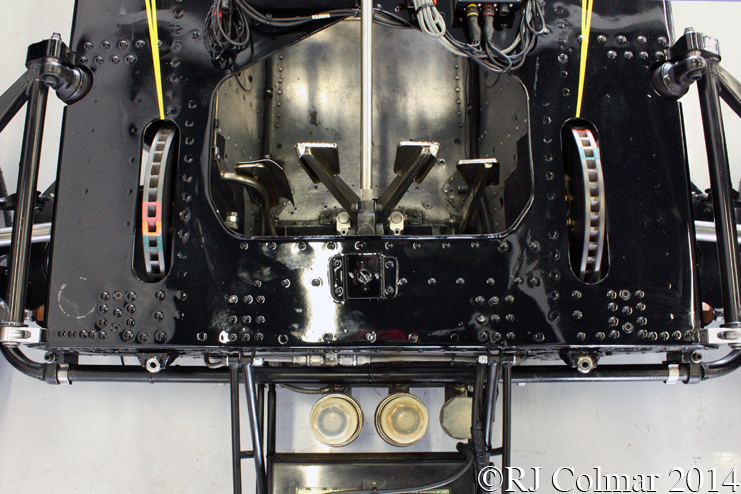
The Lotus 49 was originally built to compete in the 1967 Formula One season for drivers Jim Clark and Graham Hill. Colin Chapman had arranged for Ford to finance the building of the 3 litre / 183 cui Ford Cosworth V8 engine which like the BRM H16 Colin had used in 1966 was to be used as an integral component of the chassis, ie, if you take the motor out of the car the rear wheels would no longer be connected to the rest of the car sufficiently to be able to even push it.
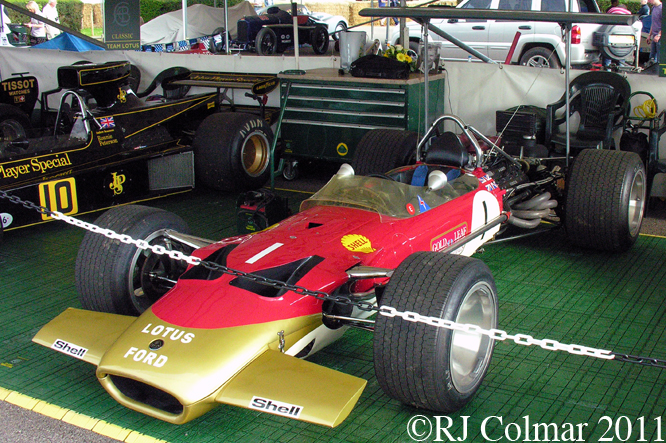

The Lotus 49 design, credited to Maurice Phillipe, was based on the 1965 Indy winning Lotus 38 which Len Terry is credited with being responsible for. Jim Clark drove the Lotus 49 to a debut win in the 1967 Dutch Grand Prix. The Type 49 in all it’s guises won 12 Grand Prix in total the last a lucky last lap win at the 1970 Monaco Grand Prix with Jochen Rindt at the wheel.
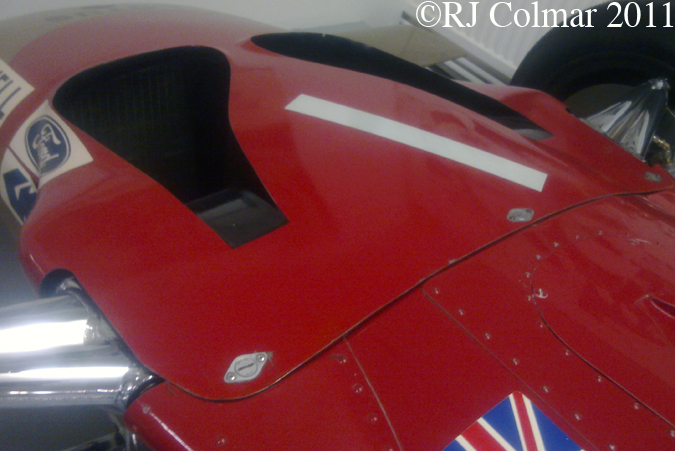

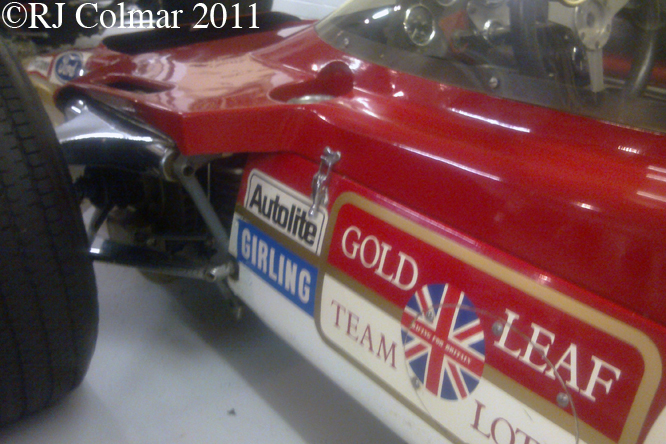
These air ducts, introduced on the 49B in 1969, allowed air to pass through the radiator and escape over the top of the car, where as on the original car the air had passed through the nose cone and out the sides of the car ahead of the front suspension units.
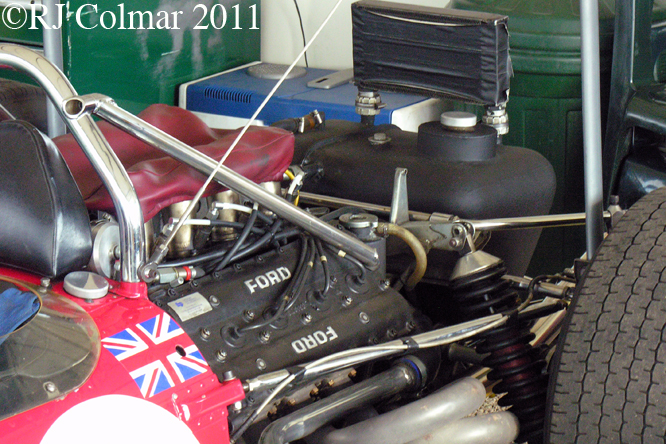
Producing around 400 hp when it first became available, Colin Chapman had an advantage over every other car in the field with the light and reliable Cosworth DFV which had years of development ahead of it that would see it’s output reach just short of 500 hp in 1985. Unfortunately, for Colin Chapman, realising that they needed to be seen running against other competitive teams Ford renegade on it’s exclusive deal with Lotus at the end of 1967 and allowed Ken Tyrrells Matra team to use Ford engines as well in 1968. By the mid 1970’s only Ferrari and BRM were the only regular runners not using Cosworth DFV’s.
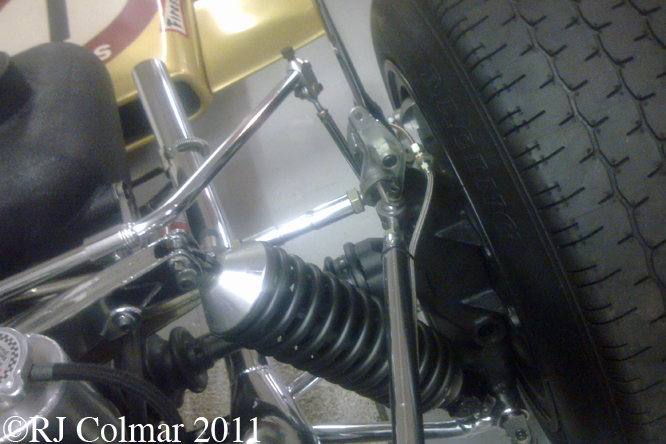

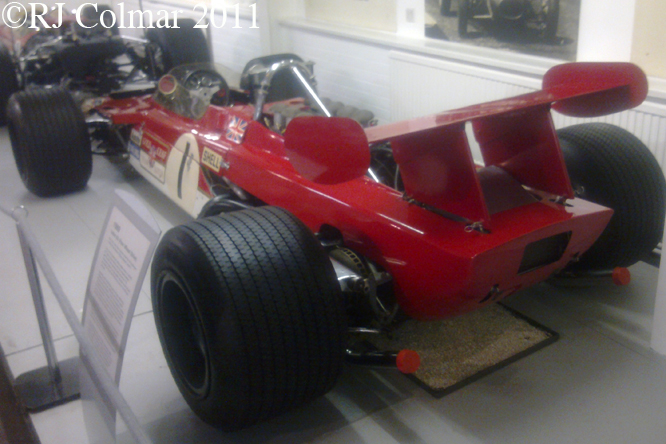
In 1968 Brabham and Ferrari copied the high aerofoil concept first seen on the Chaparral 2E Can Am car in 1966 and on the 1967 Chaparral 2F in the World Prototype championship, a month later the Lotus 49B with new rear hubs to carry the 400 lbs of downforce generated by the rear wing appeared at the French Grand Prix.
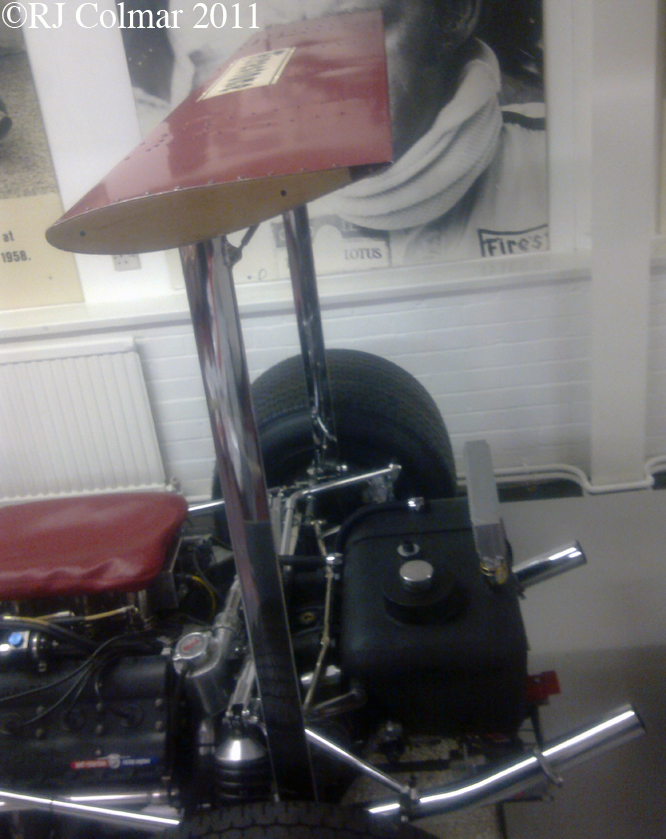

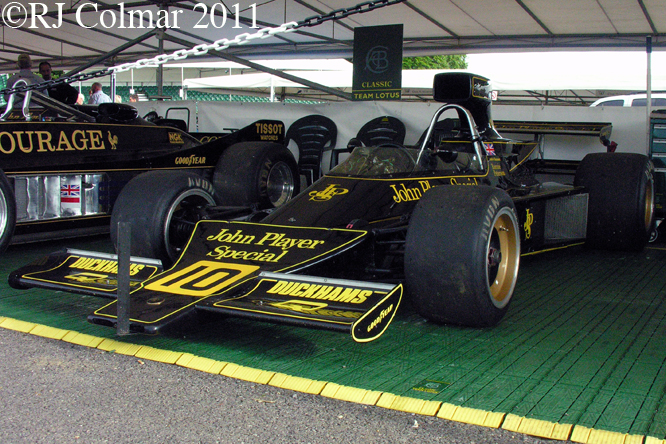
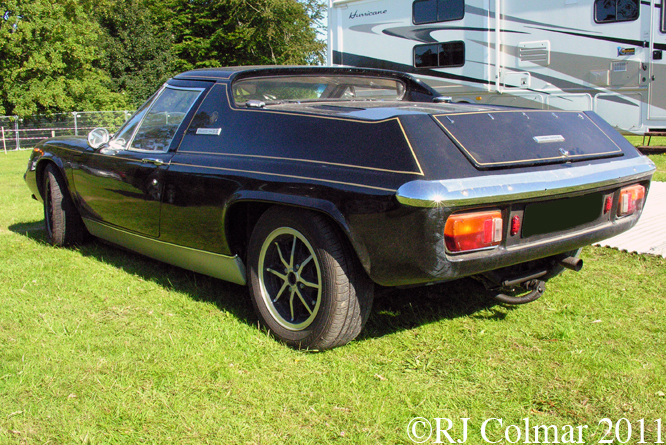
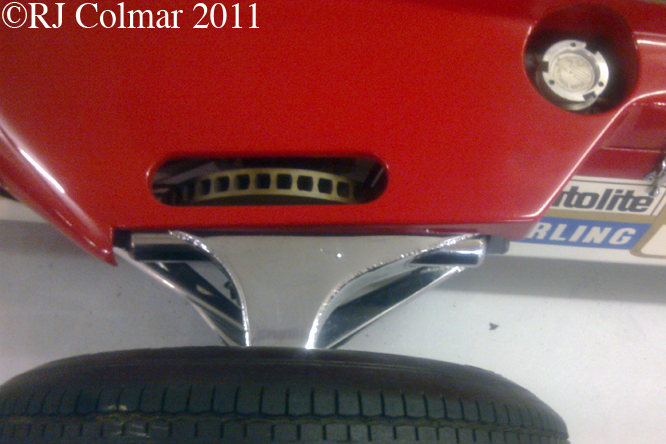
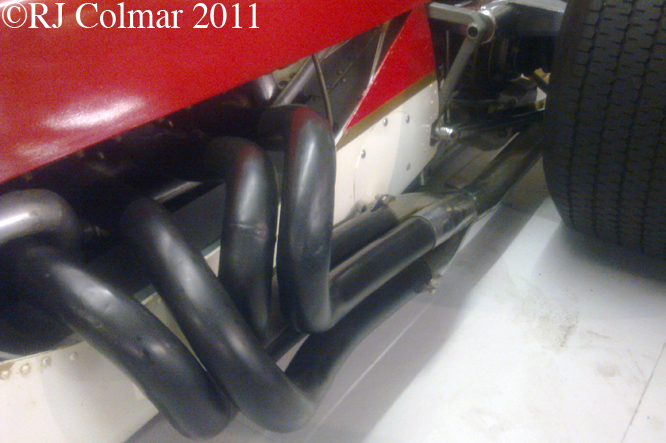
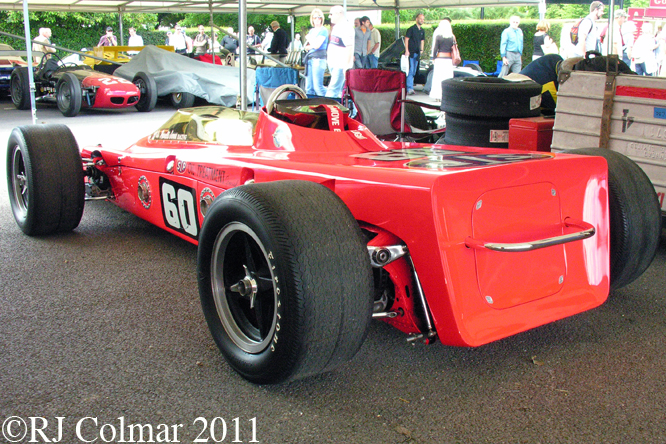
This photo shows clearly how big an issue rear grip was back in 1968 not only is their a rear wing but the Hewland gearbox is surrounded by a large oil tank in an effort to distribute as much weight to the rear of the car as possible to improve road holding.
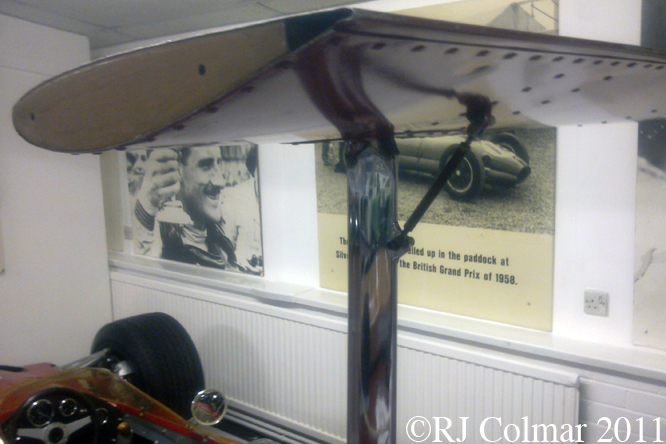

The inverted aeroplane wing shape and light construction of the rear wing can be seen here, in 1969 similar wings were attached to the front hubs as well, but two bad accidents caused by collapsing wings for Lotus Team mates Graham Hill and Jochen Rindt led to these devices being strictly controlled from the 1969 Monaco Grand Prix on.
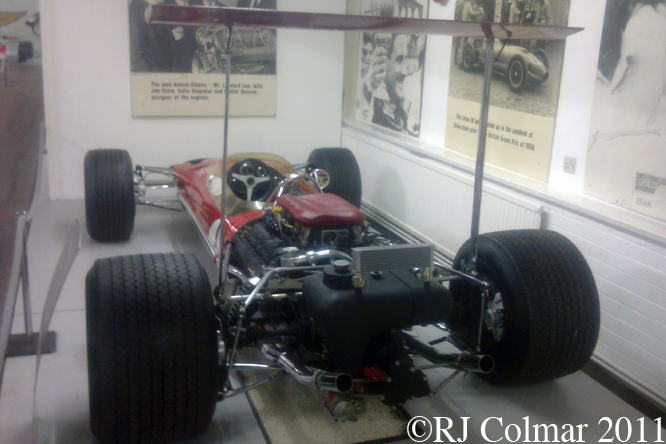

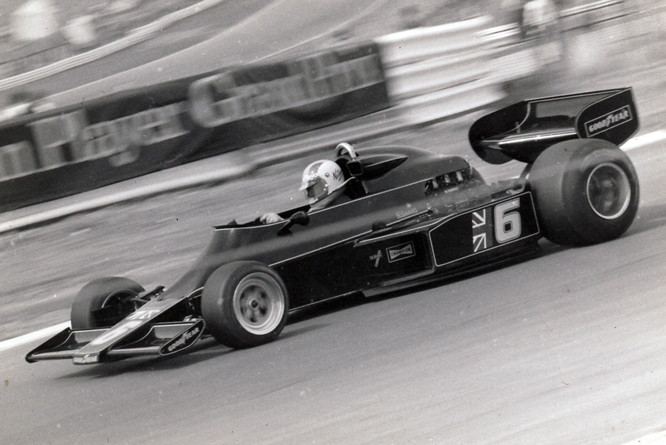
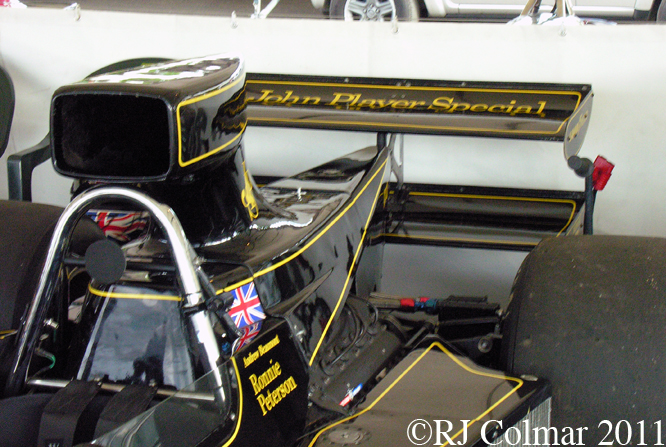
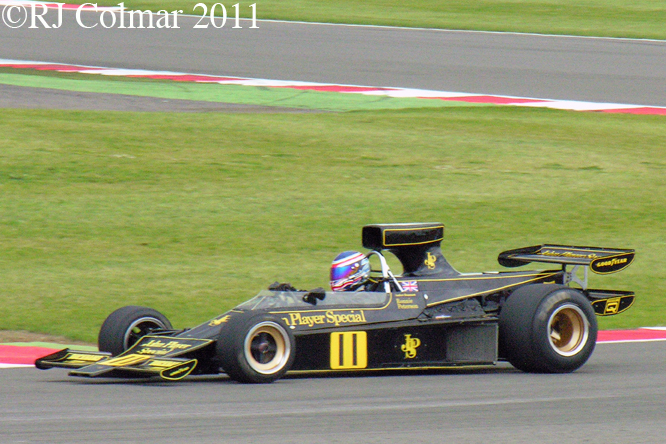
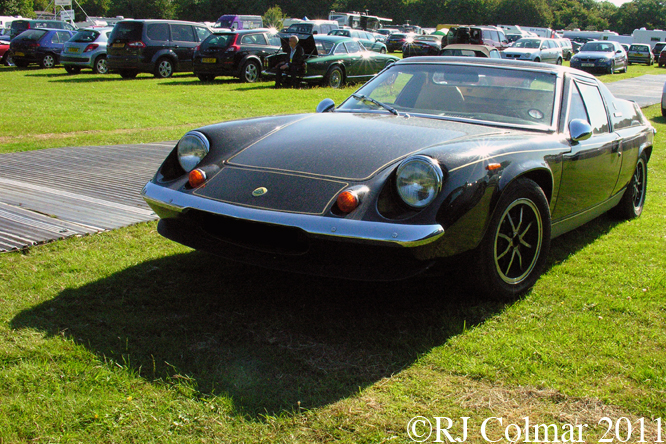
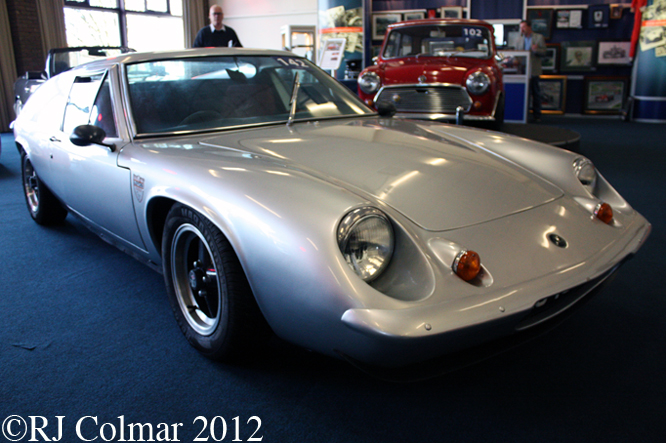
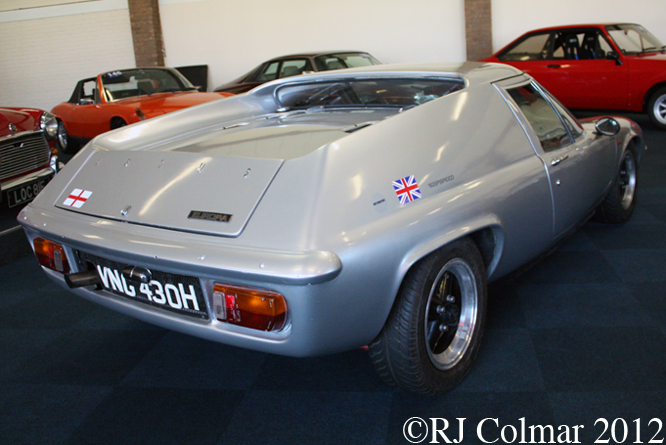
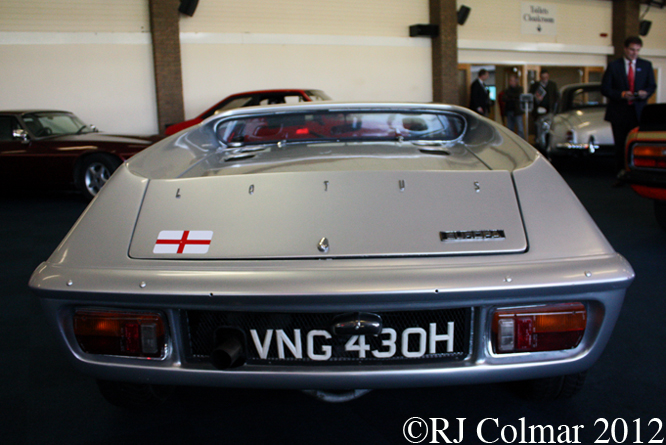
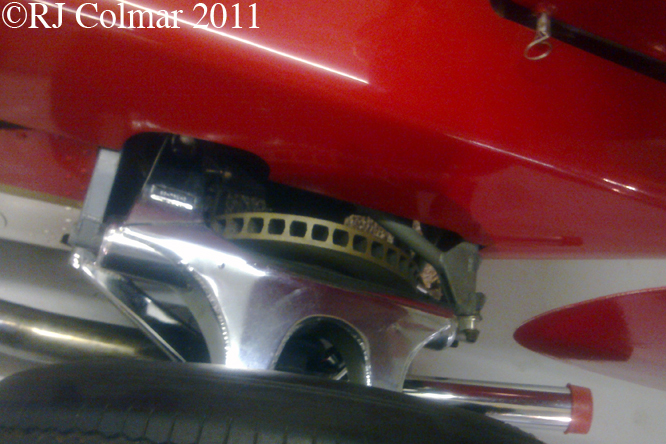
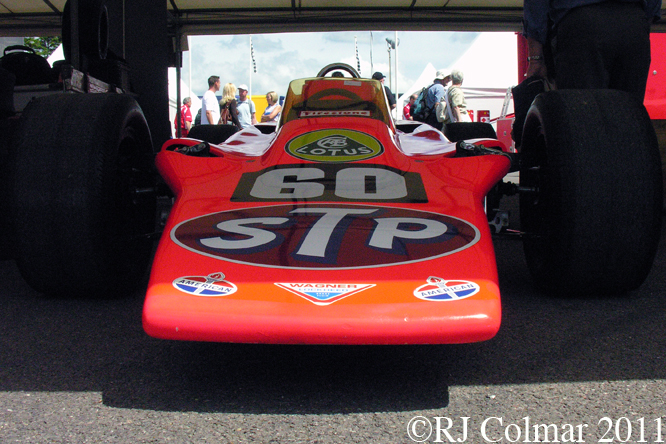
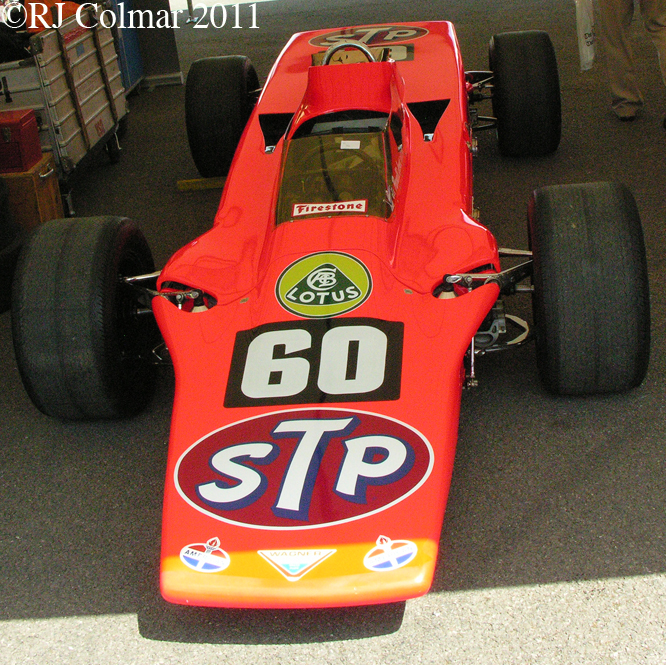
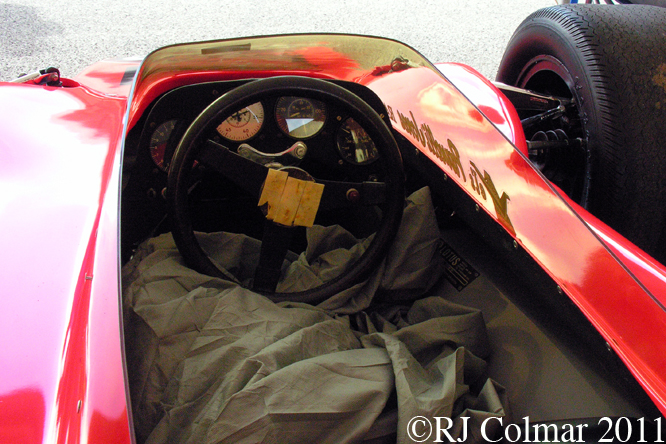
So far as I can tell the chassis seen here, in the first, second and forth photo’s, at Goodwood is #R10. Chassis R10 was probably the original 49 #R5 which for reasons that are not clear was renumbered.
While carrying the #R5 chassis plate the car was raced in his second world championship winning year by Graham Hill to win the 1968 Monaco Grand Prix, #R10 was subsequently used by 1978 World Champion Mario Andretti to win pole for his first Grand Prix start in the 1968 US Grand Prix at Watkins Glen.
Future 1970 champion Jochen Rindt was the first to use running with a 2.5 litre / 152.6 cui version of the Ford Cosworth DFV. Jochen won two Tasman Championship races in #R10.
Reigning 1968 World Champion Graham next used #R10 to win the 1969 Monaco Grand Prix. The following season Graham was driving the Lotus 49 #R7 for the privateer Rob Walker team which he crashed beyond immediate repair during practice at Monaco. Fortunately Lotus number 2 driver John Miles had failed to qualify for the race in #R10 and so it was hastily repainted in Rob Walkers colours the night before the race for Graham to drive. He finished 5th despite having broken his legs in the 1969 season ending US Grand Prix driving the same chassis just 7 months earlier !
1972 & 1974 double world champion Emerson Fittipaldi made his Grand Prix debut in Lotus Ford 49 #R10, at the British Grand Prix in 1970.
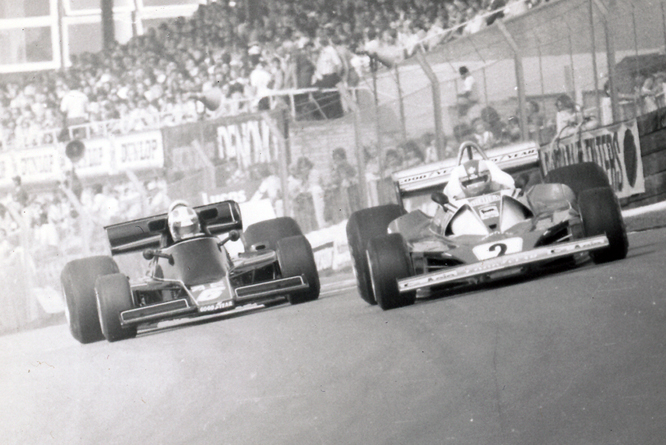
Finally the first race I ever recall seeing on TV was the 1968 British Grand Prix which was led by first Graham Hill, then his team mate Jackie Oliver before being won by Jo Siffert all three were driving Lotus 49 B’s Jo’s being the odd one out being entered by Rob Walker, who GALPOT regulars may recall had a lot of success running Stirling Moss in his Lotus 18 during the early 1960’s. Jo’s victory was the last to be recorded by a private entrant in a ‘customer’ non works customer car.
Thanks for joining me on this ‘Choice Of Champions’ edition of ‘Gettin’ a li’l psycho on tyres. I hope you will join me again tomorrow. Don’t forget to come back now !
24 04 12 PS Tim Murray has kindly pointed out that I originally incorrectly attributed the design of the Lotus 49 to Len Terry when it should have been Maurice Phillipe, apologies for any confusion. If you see an error of fact anywhere in GALPOT blogs please do not hesitate to inform me in the comments box. Thanks to Tim for the correction.
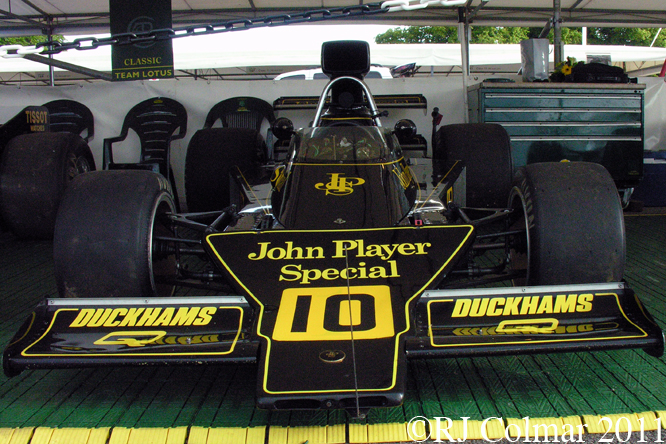
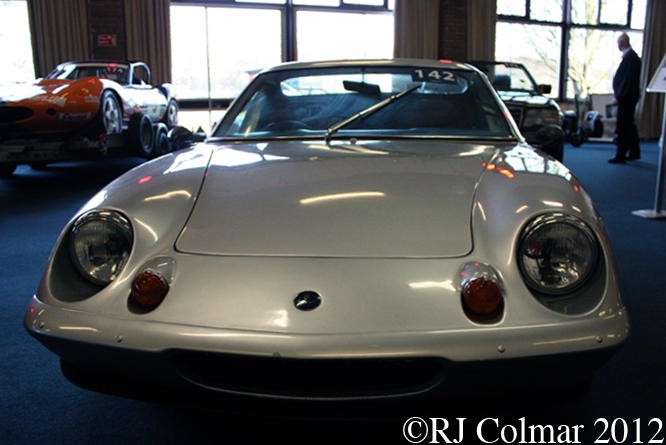
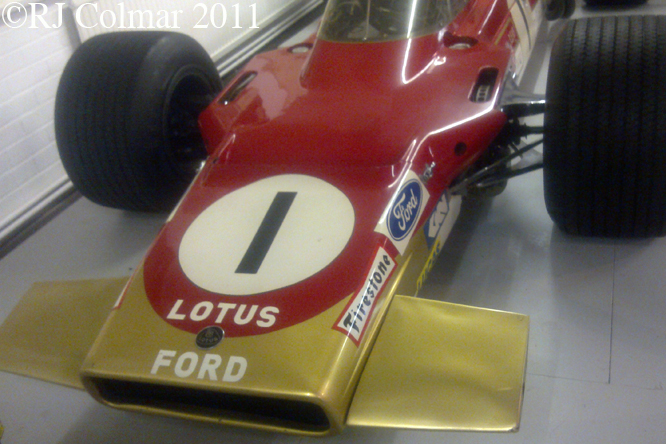
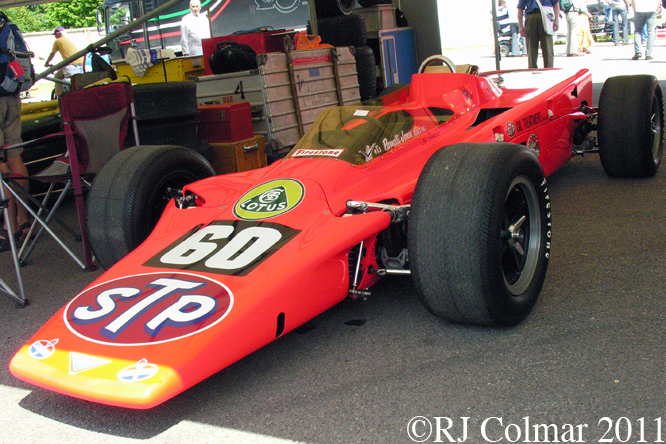
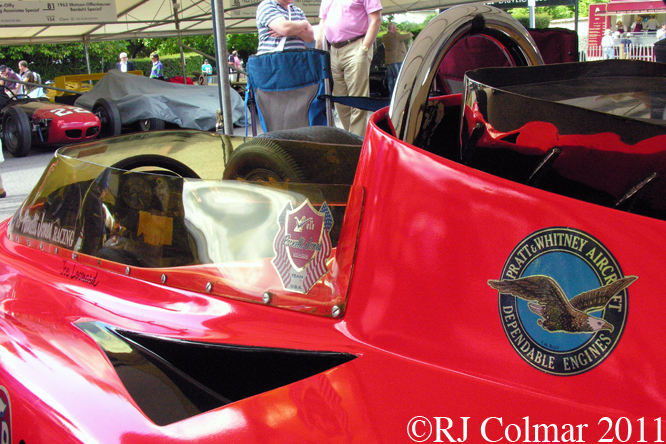
03 08 12 Serious Errata further reading of Micheal Olivers “Lotus 49 the story of a Legend” has shown that the car which is seen in the 3rd, 5th, 6th and 7th photo’s above at the Donington Collection is actually chassis #R12 and not chassis #R10 as seen in the 1st, 2nd 4th photo’s above, there are several distinguishing features which should have made this obvious at the time I originally posted this blog including the black ‘Lotus Ford’ lettering on the nose various decals and the chrome exhaust at the rear !
Chassis R12 was built up as a show car, for the Ford Motor Company, using the floor from the Lotus 49B R6/1 which was crashed by Jackie Oliver at the 1968 French Grand Prix. Built as a non runner chassis #R12 is consequently the only Lotus 49 which has never been raced, it was donated to Tom Wheatcroft’s Donington Collection when Ford no longer had a use for it.
Sincerest apologies for this error.