For the 1981 World Championship Lotus had developed the twin chassis Lotus 86 which I looked at last week, no sooner had testing of that car been finished than the ruling body of the sport outlawed the skirts on which the car depended to seal the airflow beneath the body of the car and mandated a minimum ride height.
This led to the development of the Lotus 88 which had twin chassis as did the 86 but no skirts and a 6cm minimum ride height as mandated by the new rules. Unfortunately while the governing the body of the sport accepted the Lotus 88 as legal most of the other teams did not declaring that the second outer aerodynamic chassis was a banned movable aerodynamic aid and not a fully suspended chassis.
Set against a back ground to these semantic arguments between the grandee teams of Ferrari, Renault and Alfa Romeo going up against the garagistes of Brabham, Lotus, McLaren, Williams et al made of high drama and in this instance almost every body building cars turned against Lotus in denouncing the Lotus 88 which meant that it only ever took part in a couple of practice sessions.
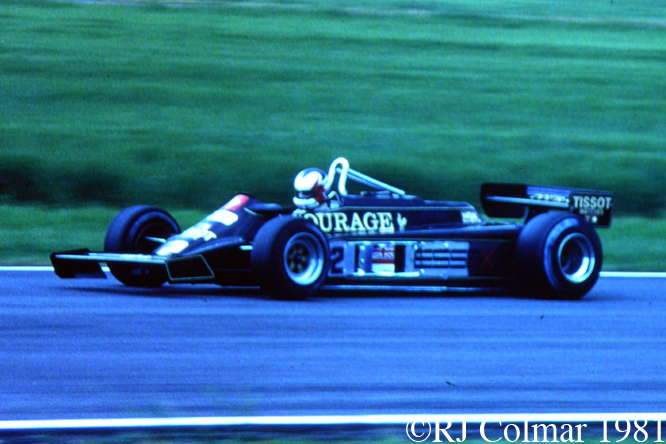
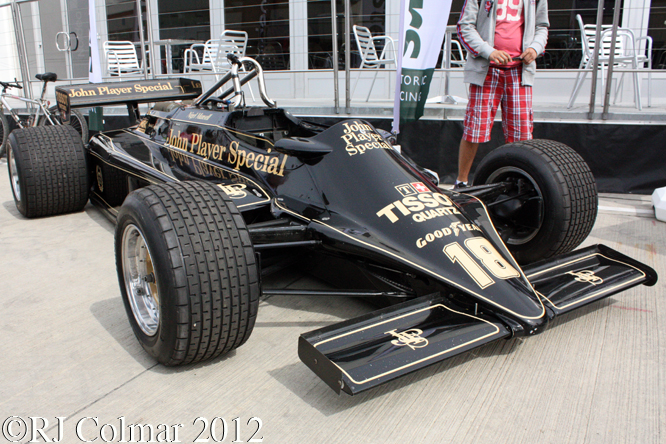
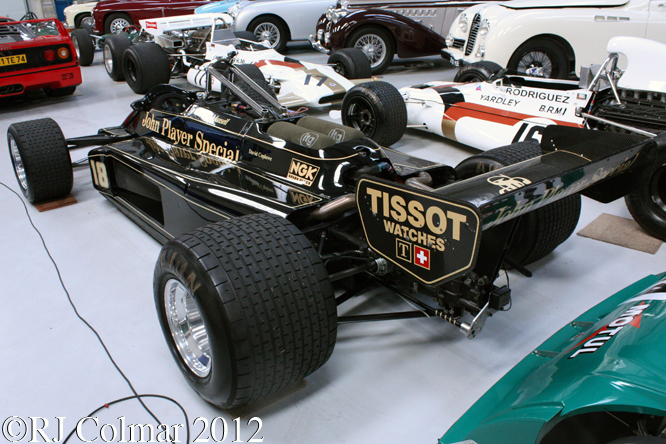
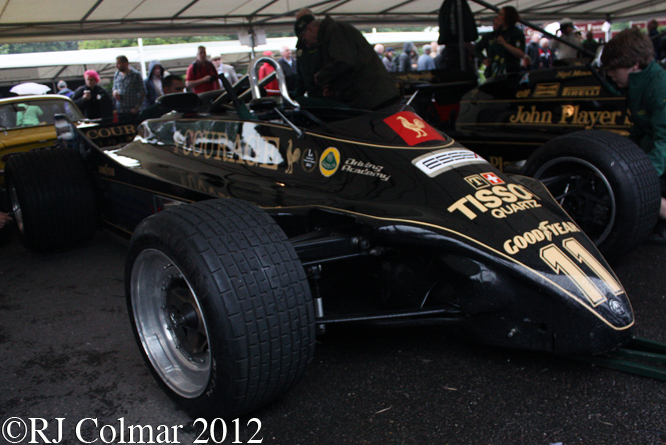
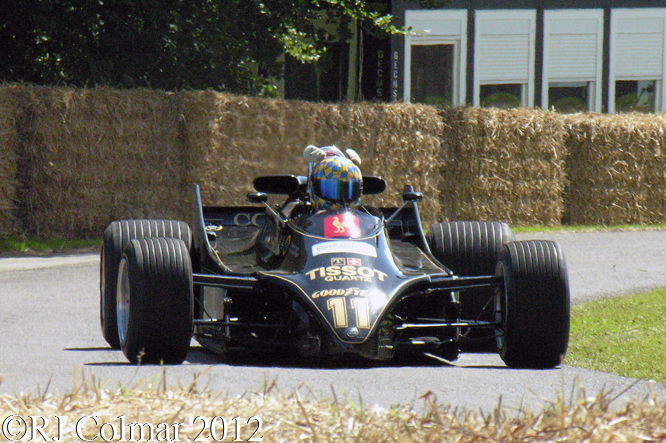
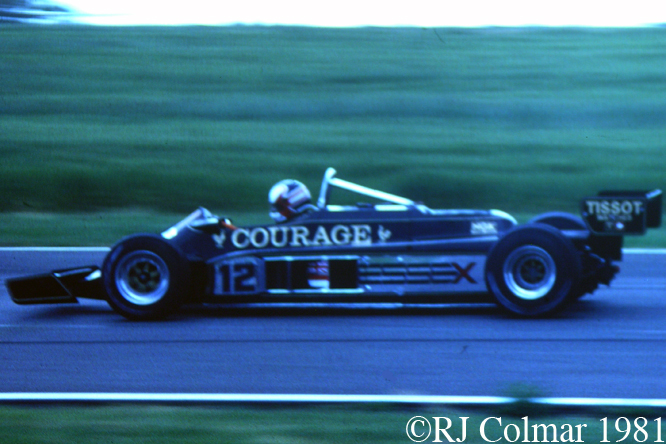
For the first half of the 1981 season Lotus were therefore forced into running the Lotus 81 from the 1980 season. By the time the Formula one circus arrived in Great Britain Lotus made one final attempt to run the Lotus 88 in practice but were again refused by their fellow competitors and so Lotus ran the 88 sans second aeroydynamic chassis and with more conventional aerodynamic side pods and wings as #87/R2 is seen being driven by Nigel Mansell during practice for the British Grand Prix at Silverstone in 1981 and #87/R4 is seen with the later front wings at Hall & Hall and in the Paddock at Silverstone during the classic meeting earlier this year.
The single chassis version of the Lotus 88 is known as the Lotus Type 87. The highlight of the Lotus 87’s half a seasons competition career was a couple of 4th place finishes, for Elio de Angeles in Italy and Nigel Mansell at Ceasers Palace.
Chassis R2 was used by Elio de Angeles in Monaco, Spain and France scoring a best 5th place finish in Spain, Mansell took the car over for the British Grand Prix and failed to qualify. There after this car was used as a spare for the remainder of the 1981 season and the first race of the 1982 season in South Africa.
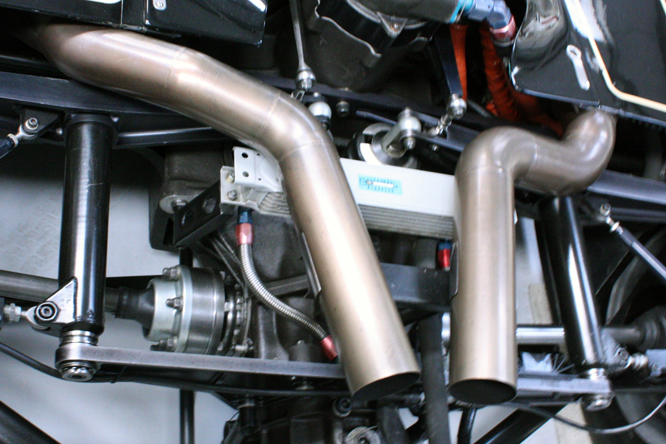
So far as I have been able to determine chassis #87/R4 seen in the more recent photo’s was driven by Nigel Mansell in at least four Grand Prix during the second half of the 1981 season. Note that the use of space age Carbon Fiber and Kevlar was becoming widespread by 1981 the following season the majority of Formula One monocoques were made from the material with the exception of Ferrari.
The absence of any bodywork around the rear suspension and exhaust shows what a rush job it was to get the Lotus 87’s to the grid most of the contemporary cars of the period had the rear axle covered in body panels by 1981 including the 1981 British Grand Prix winning McLaren MP4/1 of John Watson.
My thanks to Rick Hall if Hall & Hall for generously allowing me to take the photos of #87/R4, which is for sale, on his premises.
Thanks for joining me on this “Half A Car” edition of “Gettin’ a li’l psycho on tyres” I hope you will join me again tomorrow when I’ll be relating a Scandinavian Tale about an unusual fire engine. Don’t forget to come back now !